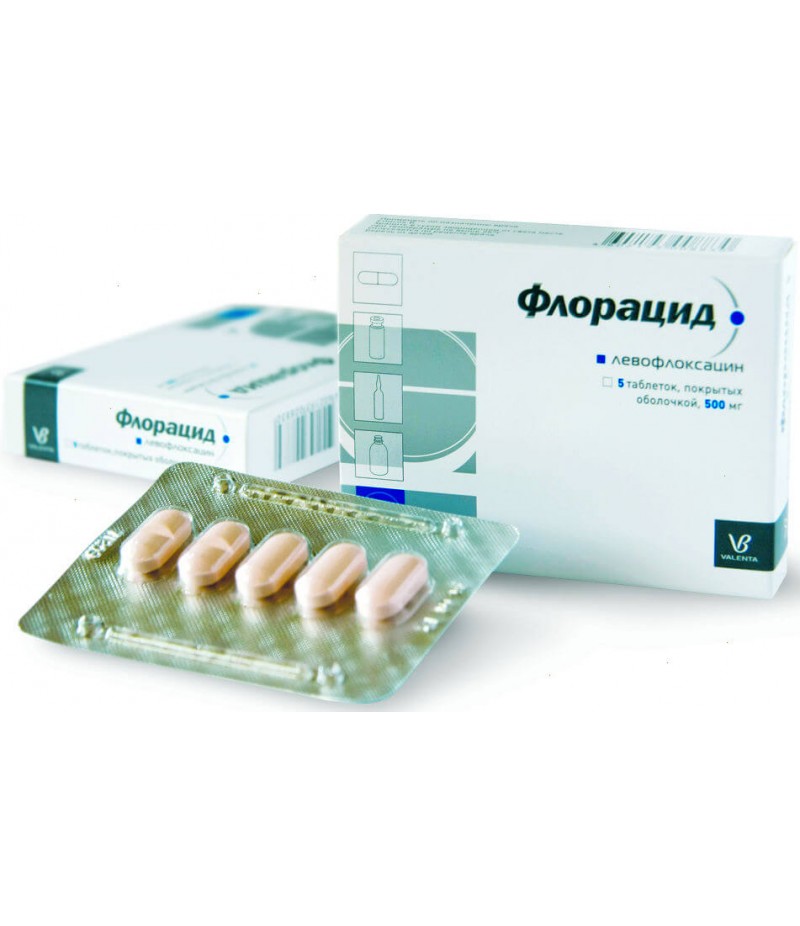
Floracyd tabs 500mg #5
- $31.95
- 3 or more $30.90
- Availability:In Stock
Floracyd antibiotic instruction for useReed more and buy Floracyd on this pageCompositionOne tablet contains 250 or 500 mg of active ingredient - levofloxacin + additional ingredients (crospovidone, sodium lauryl sulfate, MCC, mag..
Tags: tabs
Floracyd antibiotic instruction for use
Reed more and buy Floracyd on this page
Composition
One tablet contains 250 or 500 mg of active ingredient - levofloxacin + additional ingredients (crospovidone, sodium lauryl sulfate, MCC, magnesium stearate, povidone, colloidal silicon dioxide, partially hydrolyzed polyvinyl alcohol, macrogol 3350, yellow iron oxide dye, talc, red oxide dye iron, titanium dioxide, Opadry II).
Form of issue
The medicine is produced in the form of oblong, biconvex tablets, gently pink, covered with a film membrane, with a risk on one side. If you cut the tablet in half, two layers are clearly visible on the cut. The drug is sold in packages of 5 or 10 pieces.
pharmachologic effect
Antibacterial agent of a wide spectrum of action.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
A Floracyd is an antibiotic or not?
The active agent is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, a group of fluoroquinolones. It is the left-handed isomer of ofloxacin.
The substance blocks the enzymes topoisomerase 4 and topoisomerase 2 in the DNA molecule of the harmful agent. Thus, the processes of supercoiling and DNA synthesis are violated, irreversible damaging changes occur in the cytoplasm of the cell and its membrane.
The drug has a broad antibacterial spectrum. As a result of the studies it was proved that the antibiotic is active in the living body with respect to: Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Moraxella catarrhalis, Providencia rettgeri, Legionella pneumoniae, Enterobacter aerogenes, Enterococcus faecalis, Streptococcus pyogenes Viridans group streptococci, Enterobacter sakazakii, Enterobacter cloacae, Haemophilus influenzae , Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Bordetella pertussis, Citrobacter freundii, Klebsiella oxytoca, Proteus vulgaris, Providencia stuartii, Clostridium perfringens, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Enterobacter agglomerans, Streptococcus agalactiae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Chlamydia pneumoniae, Acinetobacter calcoaceticus, Citrobacter diversus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Morganella morganii, Acinetobacter anitratus, Serratia marcescens.
The agent is effective in vivo in relation to:
aerobic gram-positive organisms (Enterococcus spp., Staphylococcus spp., Staphylococcus spp., Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Streptococcus spp., etc.);
aerobic gram-negative organisms (Acinetobacter spp., Eikenella corrodens, Gardnerella vaginalis, Helicobacter pylori, Neisseria gonorrhoeae Neisseria meningitidis, Providencia spp., Pasteurella spp., Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Enterobacter spp., etc.);
anaerobic microorganisms (Bacteroides fragilis, Fusobacterium spp., Propionibacterium spp., Bifidobacterium spp., Peptostreptococcus spp., Veillonella spp., etc.);
other microorganisms (Bartonella spp., Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycobacterium spp. Mycoplasma hominis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Rickettsia spp., Chlamydia psittaci, Legionella spp.).
Levofloxacin displays moderate activity to Corynebacterium urealyticum, Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus haemolyticus Campylobacter jejuni, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicronron, Bacteroides ovatus, Porphyromonas spp. Corynebacterium xerosis, Staphylococcus epidermidis Burkholderia cepacia, Campylobacter coli, Bacteroides vulgatus, Prevotella spp.
Corynebacterium jeikeium, Staphylococcus spp. Alcaligenes xylosoxidans, Mycobacterium avium, Staphylococcus aureus are resistant to the action of the drug.
The intake of food has practically no effect on the absorption of the antibiotic. It is quickly and completely absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract, reaches a maximum concentration in the plasma after 1.3 hours. The half-life is 7 hours. Up to 40% is associated with plasma proteins. Penetrates into the urinary system, cerebrospinal fluid, alveoli, sputum and bronchial mucosa. In the liver, the drug is oxidized.
About 80% of the drug is excreted by the kidneys for two days, a small amount - through the intestine (three days).
Indications for use
The agent is prescribed for diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to the antibiotic:
with chronic bronchitis in the phase of exacerbation;
pyelonephritis and other infections of the urinary tract and kidneys, usually complicated;
prostatitis of bacterial etiology;
with intra-abdominal infection;
with acute sinusitis;
pneumonia;
with infections of the urinary tract;
for the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections;
as part of complex therapeutic procedures for resistant forms of tuberculosis.
Contraindications
The drug is contraindicated:
with epilepsy;
allergies to levofloxacin;
during pregnancy and lactation;
children and adolescents;
with lesions of joints caused by quinolones;
hypersensitivity to the drugs of the quinolone series.
Care should be taken when taking the elderly and the deficiency of glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase.
Side effects
Adverse reactions, manifested most often:
diarrhea, increased levels and activity of hepatic enzymes, nausea and vomiting (in 10% of cases);
In 1% of cases, skin itching and redness, epigastric pain, loss of appetite, dyspepsia, drowsiness, headaches, dizziness, leukopenia, asthenia and eosinophilia were observed.
Rarely and very rarely manifested:
urticaria, edema, anaphylactic reactions, vasculitis, asphyxia, bronchospasm;
Dysbacteriosis, hepatitis, blood in the feces, hypoglycemia;
depression, hallucinations, convulsions, confusion, distortion of flavors and smells, deterioration of hearing and vision;
tachycardia, vascular collapse, severe lowering of blood pressure;
tendinitis, myalgia, pain in muscles and joints, arthralgia;
disorders in the work of the kidneys, increased creatinine in the blood;
neutropenia, hemorrhages, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia;
fever and sensitivity to light.
In some cases, Stephen-Johnson syndrome, erythema, Lyell syndrome, QT interval elongation, rhabdomyolysis, pancytopenia and hemolytic anemia have been reported.
Instructions for use Floracyd (Method and dosage)
Means take inside. Drink tablets better before meals or at the time, without chewing, squeezed an abundant amount of liquid.
Duration of administration and daily dosage should be determined by the doctor depending on the nature and severity of the disease, the sensitivity of the microorganisms to the antibiotic.
According to the instructions for Floracyd, for patients with normal renal function:
to treat infections of the urinary tract take 250 mg of the drug, from 3 to 10 days, depending on the severity of the disease;
with sinusitis appoint 500 mg per day, for 10-14 days;
with prostatitis - 500 mg per day, 28 days;
During an exacerbation of a chronic bronchitis accept on 250-500 mg of an antibiotic in day, a course - 7-10 days;
for the treatment of infections of the skin and subcutaneous layer appoint 250-1000 mg of the drug per day, 7-14 days;
with pneumonia - from 500 to 1000 mg per day, one or two weeks;
for resistant forms of tuberculosis - 500 or 1000 mg funds, 90 days, in combination with other means;
at intraabdominal infections appoint 500 mg one or two weeks.
After hemodialysis or permanent outpatient peritoneal dialysis, no additional doses are required.
Antibiotic treatment lasts, at least, two days after the normalization of temperature and the reduction of the number of bacteria.
For people with kidney diseases:
if the QC value reaches 10-19 ml per minute, then you can take 125 mg 1 or 2 times a day, or once every two days;
if KK 20-50 ml / min appoint 125-250 mg 1-2 times a day;
if the SC is less than 10 ml / min, the maximum daily dosage is 125 mg.
Overdose
Symptoms of overdose are: confusion, convulsions, nausea, tachycardia, dizziness, erosion of the gastric mucosa.
As a therapy, the therapy of the manifested symptoms is performed, dialysis is ineffective, there is no antidote. It is recommended to consult a doctor.
Interaction
When combined with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and theophylline, the likelihood of seizures increases.
Preparations containing iron, sucralfates, magnesium-containing antacids, reduce the effectiveness of levofloxacin.
The risk of rupture of tendons increases significantly with the simultaneous administration of an antibiotic with SCS.
The drug does not interact with calcium carbonate.
The half-life of the agent is prolonged by the action of cimetidine and probenecid.
Various vitamin K antagonists can affect the blood coagulation system, blood tests should be monitored.
Storage conditions
Store in a dry, dark place at room temperature.
Shelf life - 2 years.
special instructions
It is not recommended to take levofloxacin with alcohol.
Elderly patients often have irregularities in the work of the kidneys, prescribe a means for them to be cautious.
After a stroke or a serious brain injury, the likelihood of seizures increases when taking an antibiotic.
When taking the drug, it does not take long to be under intense ultraviolet radiation, for example, in the sun, to avoid hypersensitivity reactions.
If there is a suspicion of pseudomembranous colitis, treatment should be stopped immediately, do not use drugs that depress GI motility.
During the treatment of pneumonia caused by pneumococci and other diseases caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, it is additionally necessary to prescribe ancillary equipment to fight the disease.
During the reception of Floracyd, it is not necessary to control the mechanisms and the machine in connection with a decrease in concentration of attention.
It should be remembered that:
in patients with a deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, hemolysis of erythrocytes can occur;
it is necessary to control coagulability of blood, when the drug is combined with antagonists of vitamin K;
in older people, the likelihood of tendinitis increases.
Reviews about Floracyd
The antibiotic has good reviews. Most reports describe improvements after urogenital infections (cystitis, urethritis, prostatitis), improvements occur as early as the second day of taking the remedy. Adverse reactions occur infrequently, mainly with improper administration of the drug or when combined with alcohol.
It should be remembered that levofloxacin is a strong antibiotic, it can not be taken without consulting a doctor.