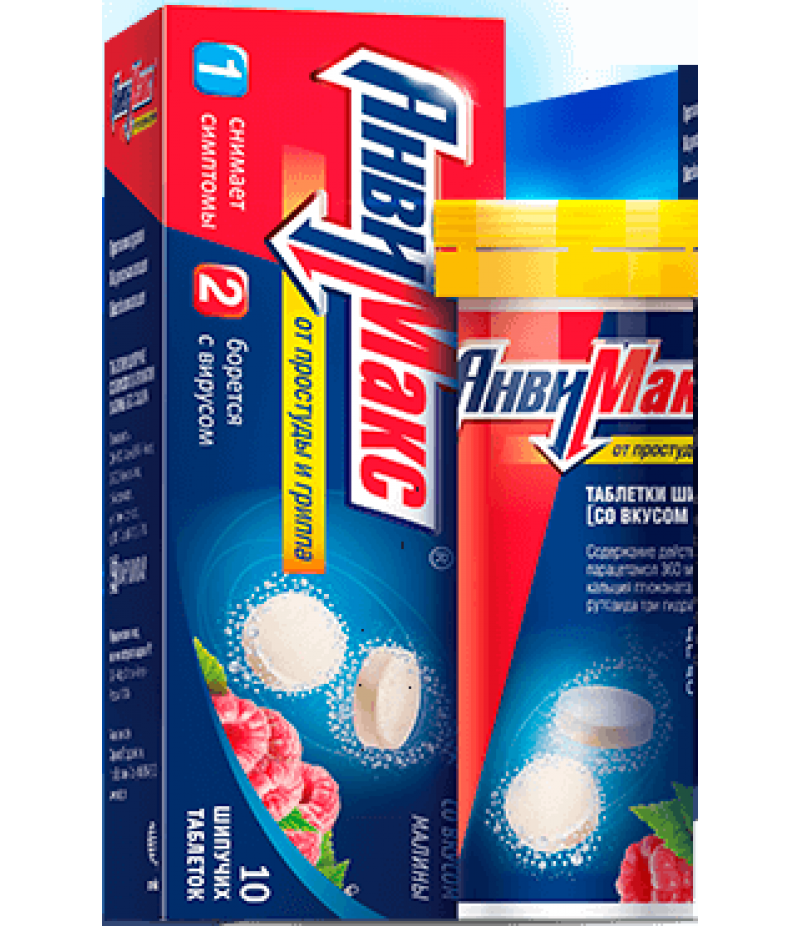
AnviMax effervescent pills #10
- $15.20
- 3 or more $14.93
- Availability:In Stock
AnviMax effervescent pills instructionYou can buy AnviMax effervescent pills hereForm of issueThe tablets are effervescent with the taste and aroma of raspberry.For 10 tablets in a tube of polypropylene complete with a lid of poly..
Tags: tabs
AnviMax effervescent pills instruction
You can buy AnviMax effervescent pills here
Form of issue
The tablets are effervescent with the taste and aroma of raspberry.
For 10 tablets in a tube of polypropylene complete with a lid of polyethylene with a silica gel insert.
1 tuba together with instructions for use in a pack of cardboard.
pharmachologic effect of Anvimax pills effervescent
Pharmacodynamics
The combined preparation has antiviral, interferonogenic, antipyretic, analgesic, antihistamine and angioprotective action.
Paracetamol has an analgesic and antipyretic effect.
Ascorbic acid is involved in the regulation of oxidation-reduction processes, promotes normal capillary permeability, blood coagulability, tissue regeneration, plays a positive role in the development of immune responses of the body, replenishes vitamin C deficiency.
Calcium gluconate, as a source of calcium ions, prevents the development of increased permeability and fragility of the vessels that cause hemorrhagic processes in influenza and acute respiratory viral infection (ARVI), has an antiallergic effect (the mechanism is unclear).
Rimantadine has antiviral activity against influenza A virus. By blocking the M2 channels of the influenza A virus, it breaks its ability to penetrate cells and release the ribonucleoprotein, thereby inhibiting the most important stage of viral replication. It induces the production of interferons alpha and gamma. With influenza caused by virus B, rimantadine exerts an antitoxic effect.
Rutoside is an angioprotector. Reduces the permeability of capillaries, swelling and inflammation, strengthens the vascular wall. It inhibits aggregation and increases the degree of erythrocyte deformation.
Loratadine - a blocker of H1-histamine receptors, prevents the development of edema of the tissues associated with the release of histamine.
Pharmacokinetics
The combined preparation has antiviral, interferonogenic, antipyretic, analgesic, antihistamine and angioprotective action.
Paracetamol. Absorption is high. Connection with plasma proteins - 15%. Penetrates through the blood-brain barrier. Metabolised in the liver in three main ways: conjugation with glucuronides, conjugation with sulfates, oxidation with microsomal enzymes of the liver. In the latter case, toxic intermediate metabolites are formed, which are subsequently conjugated to glutathione, and then to cysteine and mercapturic acid. The main isoenzymes of cytochrome P450 for this pathway of metabolism are the isoenzyme CYP2E1 (predominantly), CYP1A2 and CYP3A4 (a secondary role). With a deficiency of glutathione, these metabolites can cause damage and necrosis of hepatocytes. Additional ways of metabolism are hydroxylation to 3-hydroxyparacetamol and methoxylation to 3-methoxy-paracetamol, which are subsequently conjugated to glucuronides or sulfates. In adults, glucuronation predominates. Conjugated metabolites of paracetamol (glucuronides, sulfates and conjugates with glutathione) have low pharmacological (including toxic) activity. It is excreted by the kidneys in the form of metabolites, mainly conjugates, only 3% unchanged. In elderly patients, the clearance of Anvimax pills effervescent decreases and the half-life increases.
Ascorbic acid is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract (mainly in the jejunum). Connection with plasma proteins - 25%. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (peptic ulcer of stomach and duodenum, constipation or diarrhea, helminthic invasion, giardiasis), the use of fresh fruit and vegetable juices, alkaline drink reduce the absorption of ascorbic acid in the intestine. The concentration of ascorbic acid in the plasma is normally around 10-20 μg / ml. The time of maximum concentration in the blood plasma after ingestion is 4 hours. It easily penetrates into leukocytes, platelets, and then into all tissues; the greatest concentration is achieved in glandular organs, leukocytes, liver and lens of the eye; penetrates the placenta. The concentration of ascorbic acid in leukocytes and platelets is higher than in erythrocytes and in plasma. With deficient states, the concentration in leukocytes decreases later and more slowly and is considered as the best criterion for assessing the deficit than the concentration in the plasma. Metabolised mainly in the liver in desoxyascorbic and then in oxaloacetic acid and ascorbate-2-sulfate. It is excreted by the kidneys, through the intestine, with sweat in unchanged form and in the form of metabolites. Smoking and the use of ethanol accelerate the destruction of ascorbic acid (conversion into inactive metabolites), sharply reducing the reserves in the body. It is in hemodialysis.
Calcium gluconate. Approximately 1 / 5-1 / 3 part of the orally administered calcium gluconate is absorbed into the small intestine; this process depends on the presence of ergocalciferol, pH, dietary characteristics and the presence of factors capable of binding calcium ions. The absorption of calcium ions increases with its deficiency and the use of a diet with a reduced content of calcium ions. About 20% is excreted by the kidneys, the rest (80%) is the intestine.
Rimantadine. After oral administration, it is almost completely absorbed in the intestine. Absorption is slow. The connection with plasma proteins is about 40%. The volume of distribution is 17-25 l / kg. Concentration in nasal secretion is 50% higher than plasma concentration. Metabolised in the liver. More than 90% is excreted by the kidneys within 72 hours, mainly in the form of metabolites, 15% - in unchanged form. In chronic renal failure, the elimination half-life is 2-fold. In individuals with kidney failure and in elderly people, it can accumulate in toxic concentrations if the dose is not adjusted in proportion to the decrease in creatinine clearance. Hemodialysis has an insignificant effect on the clearance of rimantadine.
Rutozid. The time of maximum concentration in the blood plasma after ingestion is 1-9 hours. It is excreted mainly with bile and, to a lesser extent, kidneys. The half-life is 10-25 hours.
Loratadin. Quickly and completely absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. The maximum concentration in the elderly is increased by 50%. The connection with plasma proteins is 97%. Metabolized in the liver with the formation of an active metabolite of descabroxetoxyloratadine with the participation of cytochrome CYP3A4 isoenzymes and to a lesser extent CYP2D6. Does not penetrate the blood-brain barrier. It is excreted by the kidneys and with bile. In patients with chronic renal failure and during hemodialysis, the pharmacokinetics practically does not change.
Indications
Etiotropic treatment of influenza type A, symptomatic treatment of "colds", flu and ARVI, accompanied by fever, muscle pain, headache, chills in adults.
Contraindications for Anvimax pills effervescent
Hypersensitivity to one or more of the components that make up Anvimax pills effervescent; erosive-ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract in the phase of exacerbation; gastrointestinal bleeding; hemophilia; hemorrhagic diathesis; hypoprothrombinemia; portal hypertension; avitaminosis K; kidney failure; pregnancy, the period of breastfeeding; diseases of the thyroid gland, acute kidney disease, liver (acute glomerulonephritis, acute pyelonephritis, acute hepatitis, or exacerbation of chronic diseases of these organs); chronic alcoholism; hypercalcemia, expressed hypercalciuria, nephrourolythiasis, sarcoidosis, simultaneous reception of cardiac glycosides (risk of arrhythmias); intolerance to fructose; phenylketonuria.
Children under 18 years.
Precautions: Limitation of use for epilepsy, cerebral atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, hemochromatosis, sideroblastic anemia, thalassemia, hyperoxaluria, renal stone disease, dehydration, electrolyte disorders (risk of hypercalcemia), diarrhea, malabsorption syndrome, calcium nephrourolythiasis (in the anamnesis), hypercalciuria; simultaneous or during the previous 2 weeks administration of monoamine oxidase inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants; with the simultaneous administration of drugs that can adversely affect the liver (for example, inducers of microsomal liver enzymes). Care should be taken when treating patients with recurrent urate kidney stones; progressive malignant diseases; bronchial asthma.
Elderly patients with hypertension (increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke, due to the included in the preparation rimantadine).
Application Anvimax pills effervescent in pregnancy and lactation
Application during pregnancy and during breastfeeding is contraindicated.
special instructions for Anvimax pills effervescent
Duration of use - no more than 5 days.
Do not use if there are metastatic tumors.
People who are prone to ethanol use should consult a doctor before starting treatment with Anvimax pills effervescent, since paracetamol can have a damaging effect on the liver.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and other mechanisms that require increased concentration of attention: during the treatment period, care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities requiring increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Composition of Anvimax pills effervescent
Active ingredients: paracetamol - 360 mg, ascorbic acid - 300 mg, calcium gluconate monohydrate - 100 mg, rimantadine hydrochloride - 50 mg, rutoside trihydrate (in terms of rutoside) - 20 mg, loratadine - 3 mg;
Auxiliary substances: citric acid - 716 mg, sodium hydrogen carbonate - 584 mg, sorbitol - 97.85 mg, macrogol (polyethylene glycol 6000) - 75 mg, isoleucine - 75 mg, raspberry aroma (flavored food powder "Malina 909") - 75 mg , acesulfame potassium 20 mg, aspartame 20 mg, povidone (Povidone K-30) 3.75 mg, red beet red dye (E 162) 0.4 mg.
Dosing and Administration
Inside.
Dissolve the tablet in half a cup of boiled warm water. Use immediately after dissolving. Stir the solution before use.
Adults: take 1 tablet 2-3 times a day after meals for 3-5 days (not more than 5 days) until the symptoms disappear.
If there is no improvement in the state of health, stop taking the medication and consult a doctor.
Side effects
In accordance with the constituent components.
From the side of the central nervous system: increased excitability, drowsiness, tremor, hyperkinesia, dizziness, headache, "tides" of blood to the face.
From the digestive system: damage to the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum, indigestion, dryness of the mucous membrane in the mouth, lack of appetite, bloating (flatulence), diarrhea (diarrhea).
From the urinary system: moderate pollakiuria.
From the hematopoiesis: changes in blood counts. Control is needed.
Allergic reactions: angioedema, anaphylactic shock, skin rash, itching, urticaria.
From the skin: Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome) and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis.
Other: oppression of the insular pancreas function (hyperglycemia, glucosuria).
If any of the side effects listed in the manual are aggravated, or if you notice any other side effects not listed in the instructions, tell your doctor immediately.
Drug Interactions
Paracetamol reduces the effectiveness of uricosuric medicines. The concomitant use of paracetamol in high doses increases the effect of anticoagulant drugs. Inducers of microsomal oxidation in the liver (phenytoin, barbiturates, rifampicin, phenylbutazone, tricyclic antidepressants), ethanol and hepatotoxic drugs increase the production of hydroxylated active metabolites, which allows the development of severe intoxications even with a slight overdose. With simultaneous application with metoclopramide, an increase in the rate of absorption of paracetamol is possible. Long-term use of barbiturates reduces the effectiveness of paracetamol. Inhibitors of microsomal oxidation reduce the risk of hepatotoxic action.
Rimantadine enhances the exciting effect of caffeine. Cimetidine reduces the clearance of rimantadine by 18%.
Ascorbic acid increases the concentration of benzylpenicillin in the blood. Improves absorption in the intestines of iron preparations (converts trivalent iron into bivalent); can increase the excretion of iron with simultaneous use with deferoxamine. Increases the risk of developing crystalluria in the treatment of salicylates and sulfonamides short-acting, slows the excretion of kidney acids, increases the excretion of drugs that have an alkaline reaction (including alkaloids). Reduces the concentration in the blood of oral contraceptives. Increases the total clearance of ethanol, which in turn reduces the concentration of ascorbic acid in the body. With simultaneous use reduces the chronotropic effect of isoprenaline. Barbiturates and primidon increase the excretion of ascorbic acid in the urine. Reduces the therapeutic effect of antipsychotic drugs (neuroleptics) - phenothiazine derivatives, tubular reabsorption of amphetamine and tricyclic antidepressants.
Loratadin. Inhibitors of CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 increase the concentration of loratadine in the blood.
Overdose
Symptoms: during the first 24 hours after administration - pallor of the skin, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, pain in the epigastric region; disturbance of glucose metabolism, metabolic acidosis (including lactic acidosis), hypokalemia, tachycardia, arrhythmia, headache, exacerbation of concomitant chronic diseases. Symptoms of liver dysfunction may appear 12-48 hours after an overdose. In severe overdose - liver failure with progressive encephalopathy, coma; acute renal failure with tubular necrosis (including in the absence of severe liver damage). The overdose threshold can be reduced in elderly patients, in patients taking certain drugs (for example, inductors of microsomal liver enzymes), alcohol or suffering from malnutrition.
Treatment: the introduction of donors of SH-groups and precursors of the synthesis of glutathione-methionine for 8-9 hours after an overdose and acetylcysteine - for 8 hours. Gastric lavage, symptomatic therapy. The need for additional therapeutic measures (further introduction of methionine, acetylcysteine) is determined depending on the concentration of paracetamol in the blood, as well as on the time elapsed after its administration.
Storage conditions
At a temperature of no higher than 25 ° C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life - 2 years. Do not use after the expiration date printed on the package.
Terms of sell
To buy Anvimax pills effervescent you don't need a prescription.