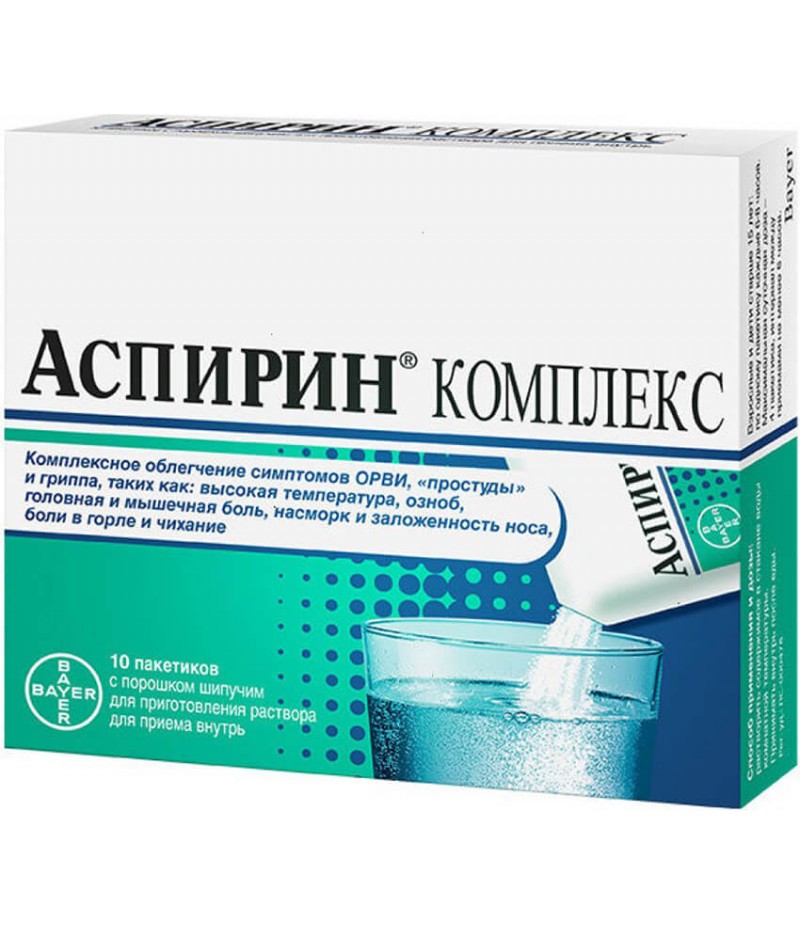
Aspirin complex powder 3547.5mg #10
- $23.89
- 3 or more $23.50
- Availability:In Stock
Aspirin complex instructionReed more and buy Aspirin complex hereCompositionEach packet contains: active ingredients: acetylsalicylic acid - 500 mg, phenylephrine hydrotartrate - 15.58 mg, chlorphenamine maleate - 2.00 mg; auxilia..
Tags: powder
Aspirin complex instruction
Reed more and buy Aspirin complex here
Composition
Each packet contains: active ingredients: acetylsalicylic acid - 500 mg, phenylephrine hydrotartrate - 15.58 mg, chlorphenamine maleate - 2.00 mg; auxiliary substances: citric acid anhydrous 1220 mg, sodium hydrogen carbonate 1709.6 mg, flavoring lemon 100 mg, dye quinoline yellow (E 104) 0.32 mg.
Packaging
10 pieces.
pharmachologic effect
Aspirin Complex is a combined preparation.
Acetylsalicylic acid has antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects, and also reduces platelet aggregation.
Phenylephrine is a sympathomimetic and, having a vasoconstrictor effect, reduces the swelling of the nasal mucous membranes and paranasal sinuses, thereby facilitating breathing.
Chlorphenamine - a blocker of histamine H1 receptors, has an antiallergic effect: itch itch (including the eye, nose), swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity, nasopharynx and sinuses, reduces the phenomenon of exudation.
Aspirin Complex, indications for use
Apply to relieve the symptoms of "colds", acute respiratory infections, flu such as: fever and chills, headache and muscle pain, runny nose and / or nasal congestion, sore throat and sneezing.
Contraindications for Aspirin Complex
acute and recurrent erosive and ulcerative gastrointestinal diseases;
hemorrhagic diathesis;
The bronchial asthma, induced by the intake of salicylates and NSAIDs;
combined use with methotrexate at a dose of 15 mg per week;
kidney failure;
liver failure;
severe heart failure in the stage of decompensation;
arterial hypertension;
angina pectoris;
an increase in the thyroid gland;
I and III trimesters of pregnancy;
lactation period (breastfeeding);
hypersensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid, other salicylates or any components of the drug.
Aspirin Complex is not prescribed for children under the age of 15 with acute respiratory infections caused by viral infections, because of the risk of developing Reye syndrome (encephalopathy and acute fatty liver disease with acute development of liver failure).
With caution should prescribe the drug for gout, hyperuricemia; patients with a history of indication of ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract (including peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum) or gastrointestinal bleeding, impaired renal and hepatic function, bronchial asthma, chronic respiratory diseases, hay fever, polyposis of the nasal mucosa ; at allergic reactions to medicines (including NSAIDs), in the second trimester of pregnancy.
Dosing and Administration
Adults and children over the age of 15 years are prescribed 1 packet every 6-8 hours. The maximum daily dose is 4 sachets, the interval between doses should be at least 6 hours.
Duration of treatment (without consulting a doctor) should not exceed 5 days when used as an anesthetic and more than 3 days - as an antipyretic.
The drug should be taken orally after a meal, previously dissolving the contents of the sachet in a glass of water at room temperature.
Application in pregnancy and lactation
Aspirin Complex contraindicated in pregnancy and lactation.
Side effects of Aspirin Complex
From the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, anorexia, pain in the epigastric region; in some cases (especially with frequent and prolonged use of the drug) - erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, latent blood loss from the gastrointestinal tract, signs of gastrointestinal bleeding (tarry stools).
From the hemopoietic system: very rarely - thrombocytopenia, anemia (due to latent bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract).
Allergic reactions: rarely (especially in patients with bronchial asthma) - skin rash, bronchospasm.
special instructions for Aspirin Complex
Children and adolescents with diseases accompanied by hyperthermia, Aspirin should be prescribed only if other drugs are ineffective. If the appointment of Aspirin has a long uninterrupted vomiting, this may be a sign of Reye's syndrome.
In patients with allergic diseases, incl. bronchial asthma, allergic and hay fever, urticaria, pruritus, mucosal edema and polyps of the nose, as well as in combination with chronic infections of the respiratory tract, in patients with increased sensitivity to analgesics and antirheumatic drugs of any type, it is possible to develop attacks of bronchial asthma.
During the period of drug use, one should refrain from drinking alcohol.
Drug Interactions
Acetylsalicylic acid
Combination with methotrexate in a dose> 15 mg per week is contraindicated. Combinations of Aspirin Complex that are used with caution: Methotrexate in a dose of less than 15 mg / week: With simultaneous use of drugs, hematological toxicity of methotrexate is increased due to the fact that NSAIDs generally reduce the renal clearance of methotrexate, and salicylags in particular displace it from the connection with plasma proteins .
Anticoagulants (coumarin, heparin): with the simultaneous administration of ASA and indirect aticoagulants, the risk of bleeding increases through the suppression of platelet function, damage to the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum and the displacement of oral anticoagulants from their association with plasma proteins.
Other NSAIDs with salicylates in a high dose (at a dose of 3 g / day or more): with the simultaneous use of drugs due to the effect of synergism increases the risk of ulcers of the gastrointestinal mucosa and bleeding.
Urikozuric drugs (probenecid, sulfinpyrazone): the therapeutic effect of uricosuric drugs is reduced due to competitive tubular elimination of uric acid.
Digoxin: with simultaneous use of drugs, the concentration of digoxin in the plasma increases due to a decrease in its excretion.
Antidiabetic drugs (insulin, sulfonylureas): the hypoglycemic effect is increased due to the fact that ASA in high dose has hypoglycemic properties and displaces sulfonylurea from the connection with plasma proteins.
Thrombolytics / antiplatelet drugs of other classes (ticlopidine): increased risk of bleeding.
Diuretics in combination with ASA at a dose of 3 g / day or more: glomerular filtration decreases, due to a reduction in the synthesis of prostaglandins in the kidneys.
Systemic glucocorticosteroids (SCS), except hydrocortisone (used to treat Addison's disease): with simultaneous use of drugs, the concentration of salicylates in the blood decreases, as the GCS enhances the elimination of salicylates.
Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: with the simultaneous use of ACE inhibitors and ASA at a dose of 3 g / day or more, the hypotensive effect of ACE inhibitors is reduced, due to a decrease in glomerular filtration.
Valproic acid: ASA disrupts the binding of valproic acid to plasma proteins, resulting in increased toxicity.
Alcohol: when combined with ASA, the damaging effect on the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract increases and the bleeding time is prolonged.
Phenylephrine
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAO inhibitors) - with the simultaneous use of phenylephrine and MAO inhibitors (antidepressants - tranylcypromine, moclobemide, anti-Parkinsonian drugs - selegiline), serious side effects can occur in the form of intense headache, increased blood pressure and body temperature.
Beta-adrenoblockers - with simultaneous use, it is possible to increase blood pressure (arterial hypertension) and severe bradycardia. Sympathomimetics with simultaneous use increases the influence of sympathomimetics on the central nervous system and cardiovascular system. Perhaps stimulation, irritability, insomnia.
Inhalational anesthetics - the use of phyllifrine before inhalation anesthesia increases the risk of heart rate abnormalities. It is necessary to stop phenylephrine treatment several days before the planned surgical treatment.
Rauwolfia alkaloids - with simultaneous use, the therapeutic effect of phenylephrine may decrease.
Caffeine - with simultaneous use, the therapeutic and toxic effects of caffeine can be enhanced.
Indomethacin, bromocriptine - in rare cases with the simultaneous use of phenylephrine with indomethacin or bromocriptine, severe arterial hypertension is possible.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors - with simultaneous use with this group of antidepressants (fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline) may increase as the sensitivity of the organism to sympathomimetics, and the risk of developing a serotonergic effect increases.
Hypotensive drugs from the group of sympatholytics, such as reserpine, guanethidine-phenylephrine, reduces the hypotensive effect of these drugs.
Chlorphenamine
Alcohol, hypnotics, tranquilizers, antipsychotics (neuroleptics), neutral analgesics-chlorphenamine can enhance the inhibitory effect of these drugs on the central nervous system.
Anticholinergic drugs (atropine, antispasmodics, tricyclic antidepressants, MAO inhibitors, antiparkinsonian drugs) - chlorphenamine enhances the anticholinergic effect of these drugs.
Overdose
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, ringing in the ears, deterioration of hearing and sight, rapid breathing, severe headache, imbalance, pronounced drowsiness, disturbance of the heart rhythm.
Treatment: gastric lavage, the appointment of activated charcoal, symptomatic therapy.
Storage conditions
Aspirin Complex should be stored at room temperature. Keep out of the reach of children. Do not use after the expiry date.
Shelf life - 4 years.
Terms of sell
To buy Aspirin Complex you don't need a prescription.