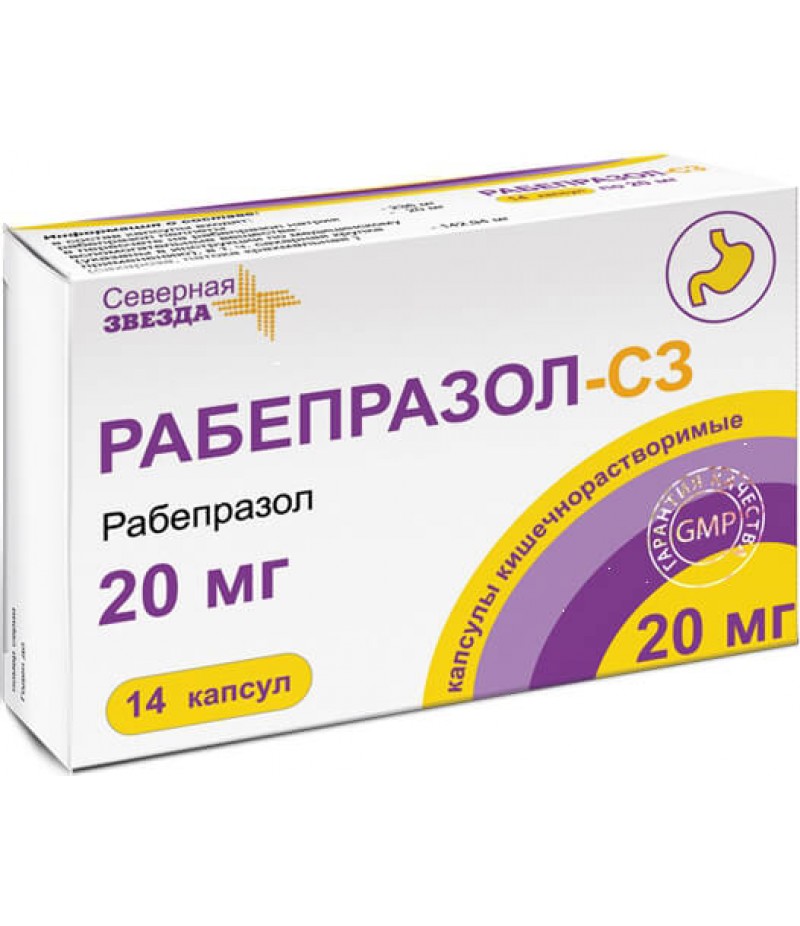
Razo tabs 20mg #30
- $21.20
- 3 or more $20.99
- Availability:In Stock
Tablets Razo instruction for useYou can buy Razo hereForm of release, composition and packagingThe tablets, covered with an enteric-coated shell from light yellow to yellow, round, biconcave, labeled with red "RB20" on one side; o..
Tags: tabs
Tablets Razo instruction for use
You can buy Razo here
Form of release, composition and packaging
The tablets, covered with an enteric-coated shell from light yellow to yellow, round, biconcave, labeled with red "RB20" on one side; on the cross section the nucleus is almost white.
1 tab.
rabeprazole sodium 20 mg
Auxiliary substances: mannitol - 97.01 mg, low-substituted giprolose - 14.4 mg, magnesium oxide heavy - 40 mg, hypromellose (5cps) - 3 mg, sodium lauryl sulfate - 1.8 mg, talc - 1.54 mg, magnesium stearate - 2.25 mg.
Sheath composition: zein - 4.9 mg, triethyl citrate - 0.49 mg.
The composition of the shell is enteric-soluble: a copolymer of methacrylic acid and ethyl acrylate [1: 1] (copolymer of methacrylic acid (type C)) - 19.28 mg, triethyl citrate - 1.92 mg, talc - 1.04 mg.
Composition of the shell: Fold yellow OY-52945 - 5.05 mg (hypromellose 5 cP - 63.65%, titanium dioxide (E171) - 28.55%, macrogol 400 - 6.3%, ferric oxide yellow oxide (E172) - 1.5%).
Composition of red ink for inscription: shellac glaze (45%) - 59%, dye red charming (E129) - 15%, butanol - 7%, ethanol denatured - 6%, titanium dioxide (E171) - 5%, propylene glycol - 4 %, isopropyl alcohol - 3%, ammonia solution concentrated 28% - 1%.
pharmachologic effect
Antiulcer drug, inhibitor of H + -K + -ATPase.
Mechanism of action
Rabeprazole belongs to the class of antisecretory compounds, which are chemically substituted benzimidazoles. Razo inhibits the activity of the enzyme H + -K + -ATPase (proton pump), thereby blocking the final stage of the synthesis of hydrochloric acid. This effect is dose-dependent and leads to inhibition of both basal and stimulated secretion of hydrochloric acid regardless of the stimulus. As a weak base, rabeprazole at any dose is rapidly absorbed and concentrated in the acidic environment of parietal cells.
Antisecretory activity
After ingestion of rabeprazole at a dose of 20 mg, the antisecretory effect develops within 1 hour. The inhibition of basal and stimulated hydrochloric acid secretion after 23 hours after the first dose of rabeprazole sodium is 62% and 82% respectively and lasts up to 48 hours. This duration of pharmacokinetic effect is much exceeds predicted by T1 / 2, which is approximately 1 hour. This effect may be explained by the binding of Razo substance to the H + -K + -ATPase of parietal cells of the stomach. The magnitude of the inhibitory effect of rabeprazole sodium on acid secretion reaches a plateau after 3 days of taking rabeprazole sodium. At the termination of reception secretory activity is restored within 1-2 days.
Effect on the concentration of gastrin in serum
At the beginning of rabeprazole therapy, the concentration of gastrin in the serum increases, which is a reflection of the inhibitory effect on the secretion of hydrochloric acid. The concentration of gastrin returns to baseline usually within 1-2 weeks after discontinuation of treatment.
Effect on enterochromaffin-like cells
The study of biopsy specimens of the bottom and antrum of the stomach in more than 500 patients receiving rabeprazole sodium or a comparator for a duration of up to 8 weeks showed no changes in the morphological structure of enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cells, the degree of gastritis, the frequency of atrophic gastritis, intestinal metaplasia or the prevalence of infection, caused by Helicobacter pylori.
In a study involving more than 400 patients receiving rabeprazole 10 mg / day or 20 mg / day for up to 1 year, the incidence of hyperplasia was low and comparable to that of patients treated with omeprazole 20 mg / day. There were no cases of adenomatous changes or carcinoid tumors observed in rats.
Other effects
At present, there is no evidence that rabeprazole causes systemic effects from the central nervous system, cardiovascular and respiratory systems. When administered orally at a dose of 20 mg for 2 weeks, rabeprazole had no effect on thyroid function, carbohydrate metabolism, and the concentration of parathyroid hormone, cortisol, estrogens, testosterone, prolactin, secretin, glucagon, FSH, LH, renin, aldosterone and growth hormone.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
Rabeprazole is rapidly absorbed from the intestine, C max in the plasma is achieved approximately 3.5 hours after taking Razo at a dose of 20 mg. The change in Cmax in plasma and the values of AUC of rabeprazole are linear in the dose range of 10 to 40 mg. Absolute bioavailability after oral administration at a dose of 20 mg (compared with the intravenous administration) is about 52%. In addition, bioavailability does not change with multiple administration of rabeprazole. Neither the time of taking Razo during the day, nor antacids affect the absorption of rabeprazole. The intake of the preparation with fatty food slows the absorption of rabeprazole by 4 hours or more, however, neither Cmax nor the degree of absorption is changed.
Distribution
The degree of binding of rabeprazole to plasma proteins is about 97%.
Metabolism
Rabeprazole is metabolized in the body in two ways. A significant part of it is metabolized systemically non-enzymatically by formation of thioester derivatives. Rabeprazole is also metabolized in the liver via cytochrome P450 to form the sulfonic and desmethyl derivatives.
Excretion
In healthy volunteers, T1 / 2 from the plasma is about 1 hour (varies from 0.7 to 1.5 hours), the total clearance is 3.8 ml / min / kg.
After a single oral intake of 20 mg of 14C-labeled rabeprazole, about 90% of Razo is excreted in the urine, predominantly in the form of a thioester of a carboxylic acid, its glucuronide and as derivatives of mercapturic acid. Unchanged drug in urine is not determined. The rest of the accepted rabeprazole is excreted through the intestine. The total excretion is 99.8%.
Pharmacokinetics in specific patient groups
In patients with stable renal insufficiency in the terminal stage, which needs maintenance hemodialysis (CC <5 ml / min / 1.73 m2), removal of rabeprazole is similar to that of healthy volunteers. AUC and Cmax in these patients were approximately 35% lower than in healthy volunteers. On average, T1 / 2 rabeprazole was 0.82 h in healthy volunteers, 0.95 h in patients during hemodialysis and 3.6 h after hemodialysis. The clearance of the drug in patients with diseases of the kidneys in need of hemodialysis was approximately 2 times higher than in healthy volunteers.
Patients with chronic compensated cirrhosis of the liver tolerate rabeprazole 20 mg once / day, although AUC is doubled and C max is increased by 50% compared to healthy volunteers.
In elderly patients, the elimination of rabeprazole is somewhat slowed down. After 7 days of taking rabeprazole in a dose of 20 mg 1 time / day in elderly people, the AUC was approximately twice as large and Cmax was increased by 60% compared to young healthy volunteers; there were no signs of cumulation of Razo.
In patients with delayed metabolism via the CYP2C19 isoenzyme after 7 days of taking rabeprazole at a dose of 20 mg / day, the AUC increases 1.9-fold, and T1 / 2 1.6-fold compared with the same parameters in "fast metabolizers", while Cmax increases on 40%.
Indications
- Stomach ulcer in the phase of exacerbation and an anastomosis ulcer;
- Duodenal ulcer in the phase of exacerbation;
- erosive and ulcerative gastroesophageal reflux disease or reflux esophagitis;
- maintenance therapy of gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- non-erosive gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome and other conditions characterized by pathological hypersecretion;
- as part of combination therapy to eradicate Helicobacter pylori in patients with peptic ulcer and duodenal ulcer or chronic gastritis.
Contraindications
- Pregnancy;
- the period of breastfeeding (lactation);
- children's age till 12 years;
- hypersensitivity to rabeprazole, substituted benzimidazoles or to the auxiliary components of the drug.
With caution should prescribe Razo in severe kidney failure, severe hepatic insufficiency, in childhood (over 12 years).
Dosage
The drug is taken orally. Tablets should be swallowed whole, without chewing or grinding. It has been established that neither the time of day nor the intake of food affects the activity of rabeprazole.
With gastric ulcer in the phase of exacerbation and ulcer of the anastomosis, it is recommended to take 20 mg 1 time per day. Usually, the cure comes after 6 weeks of therapy, but in some cases the duration of treatment can be increased.
With peptic ulcer of the duodenum in the acute phase, it is recommended to take 20 mg 1 time per day. Duration of treatment is from 2 to 4 weeks. If necessary, the duration of treatment can be increased by another 4 weeks.
In the treatment of erosive gastroesophageal reflux disease or reflux esophagitis, it is recommended to take 20 mg 1 time per day. Duration of treatment is from 4 to 8 weeks. If necessary, the duration of treatment can be increased by another 8 weeks.
With maintenance therapy of gastroesophageal reflux disease, it is recommended to take 10 mg or 20 mg 1 time per day. The duration of treatment depends on the patient's condition.
With non-erosive gastroesophageal reflux disease, it is recommended to take 10 mg or 20 mg 1 time per day.
If after 4 weeks of treatment the symptoms do not disappear, an additional study of the patient should be carried out. After relief of symptoms to prevent their subsequent occurrence, Razo should be taken by mouth at a dose of 10 mg 1 time / day as required.
For the treatment of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome and other conditions characterized by pathological hypersecretion, the dose is selected individually. The initial dose is 60 mg / day, then the dose is increased and the drug is prescribed in a dose of up to 100 mg once a day or 60 mg 2 times a day. For some patients, fractional dosing of Razo is preferred. Treatment should continue as clinical necessity. In some patients with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, the duration of treatment with rabeprazole can be up to 1 year.
For eradication of Helicobacter pylori, it is recommended to take 20 mg orally 2 times a day in a certain scheme with the appropriate combination of antibiotics. Duration of treatment is 7 days.
Correction of a dose to patients with renal insufficiency is not required.
In patients with mild and moderate hepatic insufficiency, the concentration of rabeprazole in the blood is usually higher than in healthy patients. Care should be taken when administering Razo to patients with severe hepatic impairment.
In elderly patients, dose adjustment is not required.
The safety and efficacy of rabeprazole in children aged 12 years and older is established for short-term (up to 8 weeks) treatment of GERD. The recommended dose for children aged 12 years and older is 20 mg 1 time / day for up to 8 weeks. The safety and efficacy of rabeprazole for use in other indications is not established for pediatric patients.
Side effects of Razo
Rabeprazole is usually well tolerated by patients. Side effects are generally mild or moderate and of a transient nature.
When taking rabeprazole in clinical trials, the following side effects were noted: headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea, flatulence, constipation, dry mouth, dizziness, rash, peripheral edema.
The incidence of side effects is described in accordance with the following gradation: very often (> 1/10); often (1 / 10-1 / 100); infrequently (1 / 100-1 / 1000); rarely (1 / 1000-1 / 10,000); very rarely (<1/10 000).
From the immune system: rarely - acute systemic allergic reactions.
From the hemopoietic system: rarely - thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, leukopenia.
From the side of metabolism: rarely - hypomagnesemia.
From the hepatobiliary system: rarely - increased activity of hepatic enzymes, hepatitis, jaundice, hepatic encephalopathy.
From the side of the urinary system: very rarely - interstitial nephritis.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissues: rarely - bullous rashes, hives; very rarely - erythema multiforme, toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
From the musculoskeletal system: rarely - myalgia, arthralgia.
From the genitals and the breast: very rarely - gynecomastia.
Changes in other laboratory parameters during the use of rabeprazole sodium were not observed.
When taking proton pump inhibitors, an increased risk of bone fractures may occur.
Overdose
Data on intentional or accidental overdose are minimal.
Symptoms: it was reported that the drug was taken in a dose of 60 mg 2 times / day or 160 mg once, while the side effects were minimal and reversible and did not require medical intervention.
Treatment: a specific antidote for the drug Razo is unknown. Rabeprazole binds well to plasma proteins, so it is poorly excreted in dialysis. In case of an overdose, symptomatic and supportive treatment should be performed.
Drug Interactions
In vitro studies on human liver microsomes, rabeprazole has been shown to be metabolized in the liver by the CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 isoenzymes.
Rabeprazole does not enter into clinically significant interaction with amoxicillin and other drugs metabolized by isoenzymes of the cytochrome P450 system in the liver: warfarin, phenytoin, theophylline and diazepam.
In connection with the fact that rabeprazole causes a pronounced and prolonged decline in the production of hydrochloric acid, there was an interaction with simultaneous reception with drugs, the absorption of which depends on the acidity of the contents of the stomach. In healthy volunteers, taking rabeprazole caused a decrease in the concentration of ketoconazole in the blood plasma by 30% and an increase in Cmin digoxin by 22%. With the simultaneous administration of rabeprazole with ketoconazole or digoxin, their doses should be adjusted.
With the simultaneous use of atazanavir 300 mg / ritonavir 100 mg with omeprazole (40 mg 1 time / day) or atazanavir 400 mg with lansoprazole (60 mg 1 time / day), a significant reduction in the impact of atazanavir was observed in healthy volunteers. Absorption of atazanavir depends on pH. Thus, simultaneous administration of atazanavir with proton pump inhibitors, including rabeprazole, is not recommended.
In the combined use of rabeprazole with clarithromycin, AUC and Cmax, in comparison with monotherapy, increased for rabeprazole by 11% and 34%, and for the active metabolite of clarithromycin by 42% and 46%, respectively. This effect is used in the eradication of Helicobacter pylori.
The simultaneous administration of rabeprazole and methotrexate may lead to an increase in the concentration of methotrexate and its metabolite hydroxymototrexate and increase the time of their elimination.
There was no clinically significant interaction of rabeprazole sodium with antacid preparations containing aluminum hydroxide or magnesium hydroxide.
There was no clinically significant interaction of rabeprazole with food.
special instructions for Razo
The patient's response to rabeprazole sodium therapy does not exclude the presence of malignant neoplasms in the stomach. Before and after treatment, endoscopic control is necessary to exclude malignant neoplasm, because treatment with Razo can mask the symptoms and detach the correct diagnosis.
It is recommended to be careful when first prescribing the drug Razo to patients with severe impairment of liver function.
Patients with impaired renal or hepatic function are not required to adjust the dose of Razo. AUC of rabeprazole sodium in patients with severe impairment of liver function is approximately 2 times higher than in healthy patients.
Razo does not affect the function of the thyroid gland, the metabolism of carbohydrates, the concentration in the blood of parathyroid hormone, cortisol, estrogen, testosterone, prolactin, cholecystokinin, secretin, glucagon, FSH, LH, renin, aldosterone and somatotropic hormone.
According to observational studies, proton pump inhibitor therapy may lead to an increased risk of osteoporotic fractures of the hip, wrist, spine. The risk of fractures was increased in patients who received proton pump inhibitors in high doses for 1 year or more.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and manage mechanisms
Based on the peculiarities of pharmacodynamics of rabeprazole and its profile of undesirable effects, it is unlikely that the Razo drug affects the ability to drive vehicles and perform other activities requiring concentration of attention and speed of psychomotor reactions. However, in the case of drowsiness and dizziness, these activities should be avoided.
Pregnancy and lactemia
There are no data on the safety of rabeprazole during pregnancy. Studies of reproductive performance in rats and rabbits showed no signs of impaired fertility or fetal developmental defects caused by rabeprazole; However, in rats in small quantities, the drug penetrates the placental barrier. Rabeprazole should not be used during pregnancy, except when the expected positive effect on the mother exceeds the potential risk to the fetus.
It is not known whether rabeprazole is excreted in breast milk. Appropriate studies in lactating women were not conducted. However, rabeprazole is found in the milk of lactating rats, so Razo should not be used during breastfeeding.
Application in childhood
With caution should be prescribed in childhood (over 12 years).
Contraindicated use of the drug in childhood to 12 years.
In case of violations of kidney function
With caution should prescribe Razo in severe kidney failure.
With violations of liver function
With caution should prescribe the drug in severe hepatic insufficiency.
Application in old age
In elderly patients, dose adjustment is not required.
Conditions of leave from pharmacies
You don't need a prescription to buy Razo tablets.
Terms and conditions of storage
Razo should be stored out of reach of children at a temperature of no higher than 25 ° C.