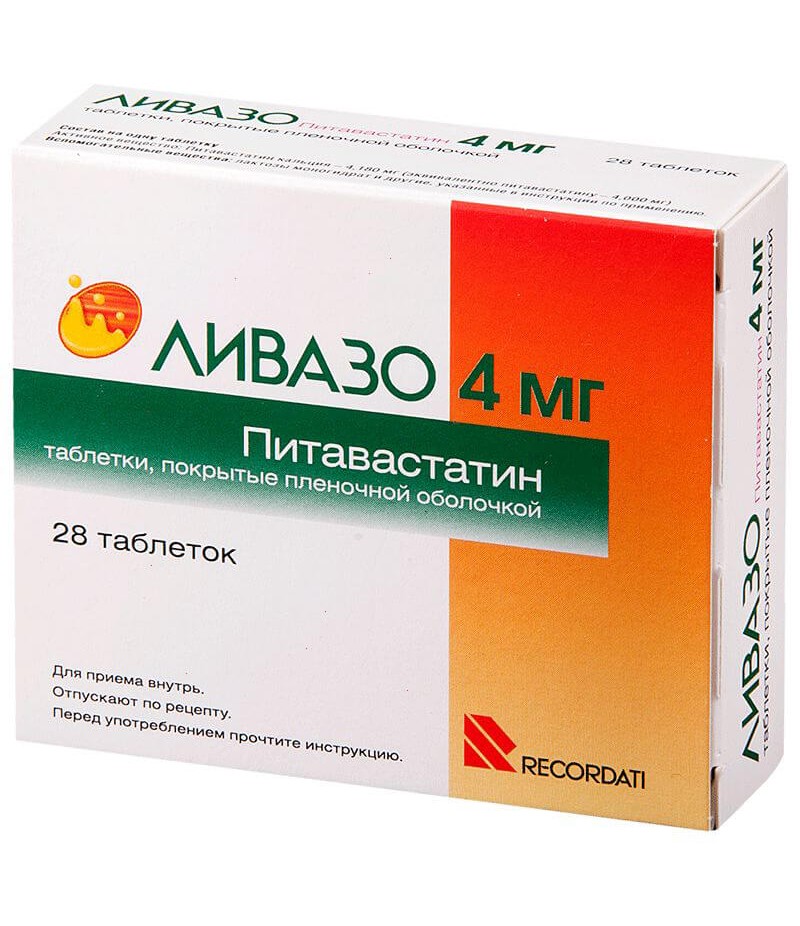
Livazo tabs 4mg #28
- $38.65
- 3 or more $37.99
- Availability:In Stock
Livazo instruction for useYou can buy Livazo hereThe composition and release form of the drugTablets, film-coated white, round, biconvex, cross-section core of white; on one side of the tablet - engraving "KC", on the other - engr..
Tags: tabs
Livazo instruction for use
You can buy Livazo here
The composition and release form of the drug
Tablets, film-coated white, round, biconvex, cross-section core of white; on one side of the tablet - engraving "KC", on the other - engraving "4".
1 tab.
pitavastatin calcium 4.18 mg,
which corresponds to the content of pitavastatin 4 mg
Excipients: lactose monohydrate - 252.34 mg, low-level hyprolosis - 50.16 mg, hypromellose - 5.32 mg, magnesium aluminometasilicate - 6.4 mg, magnesium stearate - 1.6 mg.
The composition of the film shell: Opadry white - 9 mg, including hypromellose - 5.952 mg, titanium dioxide - 2.409 mg, triethyl acetate - 0.594 mg, colloidal silicon dioxide - 0.045 mg.
pharmachologic effect
Competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase. the enzyme catalyzing the initial stage of cholesterol synthesis is the formation of mevalonic acid from HMG-CoA. Since the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic acid is the initial stage of cholesterol synthesis, the use of pitavastatin does not cause the accumulation of potentially toxic sterols in the body. HMG-CoA is easily metabolized to acetyl-CoA. which is involved in many processes of synthesis in the body. Clinical studies have shown the effectiveness of pitavastatin in reducing the concentration of total cholesterol (OXC) in plasma, LDL cholesterol (LDL cholesterol), cholesterol-VLDL, triglycerides (TG) and apolipoprotein B (apo-B). as well as increasing the concentration of HDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein A1 (Aro-A1).
Pharmacokinetics
Pitavastatin is rapidly absorbed in the upper GI tract, Cmax in the blood plasma is reached within 1 hour after taking Livazo. Food intake does not affect absorption. Cmax of pitavastatin in plasma decreases by 43% when taken together with fatty foods, but the AUC remains unchanged. Unchanged pitavastatin undergoes enterohepatic circulation and is well absorbed from the jejunum and ileum. Absolute bioavailability of pitavastatin 51%.
More than 99% of pitavastatin binds to plasma proteins, mainly albumin and alpha-1 acid glycoprotein. Average Vd 133 liters. Pitavastatin actively penetrates hepatocytes using the OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 transport proteins. AUC varies n within 4-fold increase from minimum to maximum value. Pitavastatin is not a substrate for P-glycoprotein.
Plasma contains mostly unchanged pitavastatin. The main metabolite is an inactive lactone, which is formed from a pitavastatin glucuronide ether type conjugate with the participation of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT1A3 and 2B7). Cytochrome P450 affects the metabolism of pitavastatin minimally. CYP2C9 isoenzyme (and to a lesser extent CYP2C8 isoenzyme) is involved in the metabolism of pitavastatin to secondary metabolites.
Pitavastatin in unchanged form is rapidly excreted from the liver with bile, but undergoes enterohepatic recirculation, ensuring its long-lasting effect. Less than 5% of pitavastatin is excreted by the kidneys. T1 / 2 of plasma varies from 5.7 h (single dose) to 8.9 h (in equilibrium), the average clearance is 43.4 l / h after a single dose.
Indications
Primary hypercholesterolemia, including heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (hyperlipidemia type II, according to Fredrickson classification) or mixed hypercholesterolemia (hyperlipidemia type IIb according to Fredrickson classification), hypertriglyceridemia (type IV hyperlipidemia and Fredrikson classification, and asst as a group, and as a group, I’m now), and I’m in-laws, and I’m now, as a group of non-afflicts, and as a group of non-afflicts, and as a group of non-afflicts, and as a group of non-afflicts, and as a group of in-laws, and as a group of in-laws, and already in-laws, and as a group of subjects, I will act as an ally, and as a group, I will act as a group of households, including hyperdiglyceridemia (type IV hyperlipidemia and Fredrikson class, and I will be already and I will not need to apply), and I will be in line with 201, and I will be in line with the 201 st5. for example, exercise, weight loss) are insufficient.
Contraindications for Livazo
Severe hepatic impairment (more than 9 points on the Child-Pugh scale) or class C according to the Child-Pugh classification, liver disease and the active phase, including a persistent increase in the activity of hepatic transaminases in the blood serum (more than 3 times compared to VGN); myopathy; simultaneous administration of cyclosporine; pregnancy, breastfeeding, lack of adequate methods of contraception in women of childbearing age; age under 18 years (efficacy and safety not established); Hypersensitivity to pitavastatin, auxiliary components of Livazo and other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins).
Dosage
Inside Initial dose - 1 mg 1 time / day. If necessary, increase the dose at intervals of at least 4 weeks to 2 mg / day. The dose should be selected individually in accordance with the concentrations of LDL cholesterol, the purpose of treatment and the patient's response to treatment. Most patients require a dose of 2 mg. The maximum daily dose is 4 mg.
Patients with mild and moderate liver dysfunction: a maximum daily dose of 2 mg is recommended.
Patients with impaired renal function: in case of impaired renal function of mild severity (it is desirable to objectively evaluate this degree with a reflection of QA or GFR), pitavastatin should be used with caution. Data on the use of a maximum daily dose of 4 mg for kidney dysfunction of any severity are limited, so it is necessary to prescribe a maximum daily dose of 4 mg only with careful monitoring of renal function after gradually increasing the dose. It is not recommended for patients with severely impaired renal function to prescribe a maximum daily dose of 4 mg; It is recommended to consider limiting the maximum daily dose to 2 mg in severe renal failure.
Side effects of Livazo
From the hemopoietic system: infrequently - anemia.
From the side of metabolism: infrequently - anorexia.
Mental disorder: often - insomnia.
On the part of the nervous system: often - headache; infrequently - dizziness, taste disturbance, drowsiness.
From the senses: infrequently - ringing in the ears; rarely - reduced visual acuity.
On the part of the skin: infrequently - pruritus, soup; rarely - urticaria, erythema.
From the musculoskeletal system: often - myalgia, arthralgia; infrequently - muscle spasms; rarely - myopathy, rhabdomyolysis.
From the urinary system: infrequently - pollakiuria.
On the part of the digestive system: often - constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia, nausea; infrequently - abdominal pain, dry oral mucosa, vomiting; rarely - glossy, acute pancreatitis, abnormal liver function, cholestatic jaundice.
Laboratory indicators: infrequently - increased activity of "liver" transaminases ACT, ALT, increased activity of CPK.
Other: infrequently - asthenia, malaise, fatigue, peripheral edema.
Drug interactions
Pitavastatin is actively transported into the human hepatocyte by numerous hepatic transporters (including the Organic Anion Transport Polypeptide (OATP)), which may be included in some of the following interactions.
Cyclosporin: simultaneous administration of a single dose of cyclosporine with pitavastatin in an equilibrium state leads to a 4.6-fold increase in the AUC of pitavastatin is unknown. Contraindicated use in patients receiving treatment with cyclosporine.
Erythromycin: co-administration of erythromycin with pitavastatin results in a 2.8-fold increase in pitavastatin AUC. Recommended temporary discontinuation of pitavastatin intake during treatment with erythromycin or other macrolide antibiotics.
Hemfibrozol and other fibrates in rare cases monotherapy with fibrates was associated with the development of myopathy. The simultaneous use of fibrates with statins was associated with an increase in the incidence of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis. Caution should be exercised while applying pitavastatin with fibrates. In pharmacokinetic studies, the simultaneous use of pitavastatin with gemfibrozil resulted in a 1.4-fold increase in pitavastatin AUC and an increase in fenofibrate AUC by a factor of 1.2.
Nicotinic acid (in lipid-lowering doses): a study of the interaction in the treatment with pitavastatin and nicotinic acid in lipid-lowering doses (more than 1 g / day) was not conducted. The use of nicotinic acid in monotherapy has been associated with the development of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis. Therefore, when used simultaneously with nicotinic acid in lipid-lowering doses (more than 1 g / day), pitavastatin should be used with caution.
Fusidic acid: severe muscle disorders such as rhabdomyolysis, which are attributed to the interaction between fusidic acid and statins, have been reported. During treatment with fusidic acid, it is recommended to temporarily discontinue the use of pitavastatin.
Rifampicin: co-administration with pitavastatin resulted in a 1.3-fold increase in pitavastatin AUC.
Ezetimibe and its glucuronide metabolite inhibits the absorption of dietary and biliary cholesterol. The simultaneous use of pitavastatin did not affect the plasma concentrations of pitavastatin.
CYP3A4 isoenzyme inhibitors: studies of interaction with itraconazole and grapefruit juice, known inhibitors of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme, have not revealed a clinically significant interaction on plasma concentrations of pitavastatin.
Digoxin, a known substrate of P-glycoprotein (Pgp), does not interact with pitavastatin. When used together, no significant changes in plasma concentrations of pitavastatin or digoxin were observed.
Warfarin: the equilibrium state of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics (INR and prothrombin time (PT)) of warfarin in healthy volunteers did not change when co-administration of warfarin with pitavastatin 4 mg daily. However, as with the use of other statins, patients receiving warfarin, when added to the treatment of pitavastatin, should be monitored for PV and INR.
special instructions
Use Livazo with caution if there is a risk of myopathy / rhabdomyolysis - renal failure, hypothyroidism, personal or family history of hereditary muscular diseases and previous history of muscular toxicity when using other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors or fibrates, excessive alcohol consumption, age over 70, diseases liver history.
Patients should be warned to report any muscle symptoms. The activity of CPK should be determined in any patient reporting muscle pain, muscle soreness on palpation or weakness, especially if this is accompanied by indisposition or fever.
The activity of CPK should not be determined after physical exertion or if there are any other possible reasons for the increase in CPK that may distort the result. With an increase in CPK activity (5 times higher than VGN), a control analysis should be performed within 5-7 days.
Use Livazo with caution in patients with predisposing factors for the development of rhabdomyolysis. The activity of CPK should be determined to establish a control baseline value in the following cases: renal failure; hypothyroidism; personal or family history of hereditary muscular diseases; previous history of muscular toxicity when treated with fibrates or other statins; a history of liver disease or alcohol abuse; elderly patients (starting 70 years) with other predisposing risk factors for the development of rhabdomyolysis. In such cases, clinical monitoring is recommended, and the risk of treatment should be considered depending on the potential benefits. Treatment should not begin if CPK is 5 times higher than VGN.
The patient should be advised to immediately inform the doctor about muscle pain, weakness, or cramps. The activity of CPK should be determined, and treatment should be stopped if the activity of CPK is increased (5 times higher than VGN). It should be considered, the question of stopping treatment when severe muscular symptoms occur, even if the activity of CPK does not exceed VGN 5 times. When resolving the symptoms and returning the activity of CPK to normal, the question of reappointment at a dose of 1 mg can be considered, while observing close monitoring.
Like all statins, pitavastatin should be used with caution in patients with a history of liver disease, or in patients who regularly consume excessive amounts of alcohol. Before starting treatment with pitavastatin, and then periodically during treatment, functional liver function tests should be performed. In patients with a persistent increase in liver transaminase activity (ALT and ACT), 3 times more than VGN, treatment with pitavastatin should be discontinued.
Use with caution in patients with moderate to severe renal failure. Increase the dose should be only with careful monitoring. A dose of 4 mg is not recommended for patients with severe renal failure.
Some evidence suggests that statins, as a class, cause an increase in glucose concentration in the blood, and in some patients with a high risk of developing diabetes mellitus can lead to a level of hylerglycemia, which requires appropriate treatment of diabetes. However, this danger is offset by a reduction in vascular risk with statin treatment, and therefore should not be a reason for stopping treatment with statins. Patients who are at risk of developing hyperglycemia (fasting glucose concentration from 5.6 to 6.9 mmop / l, BMI> 30 kg / m2, elevated TG concentration, arterial hypertension) should be subjected to clinical and biochemical control in accordance with national guidelines.
Rare cases of interstitial lung disease were recorded with the use of certain statins, especially with long-term therapy. Observed clinical signs include shortness of breath, an unproductive cough, and worsening of general health (fatigue, loss of body weight, and fever). If interstitial lung disease is suspected, statin therapy should be discontinued.
Influence on ability to drive vehicles and mechanisms
Care must be taken when driving or doing other work that requires increased attention, since such adverse reactions as dizziness and drowsiness may develop.
Pregnancy and lactation
Contraindicated use during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding).
Use in childhood
It is forbidden to use Livazo in patients under the age of 18 years (since efficacy and safety have not been established).
In case of impaired renal function
With caution should use Livazo for renal failure. Data on the use of a maximum daily dose of 4 mg for kidney dysfunction of any severity are limited, so it is necessary to prescribe a maximum daily dose of 4 mg only with careful monitoring of renal function after gradually increasing the dose. It is not recommended for patients with severely impaired renal function to prescribe a maximum daily dose of 4 mg; It is recommended to consider limiting the maximum daily dose to 2 mg in severe renal failure.
With abnormal liver function
A maximum daily dosage of 2 mg is recommended for patients with mild and moderately impaired liver function.
It is forbidden to use a drug with severe liver failure (more than 9 points on the Child-Pugh scale) or class C according to Child-Pugh classification, liver diseases in the active phase, including a persistent increase in the activity of hepatic transaminases in the serum (more than 3 times compared to VGN).
Use in old age
Elderly patients dose adjustment is not required.
Pharmacy sales terms
You don't need a prescription to buy Livazo.
Terms and conditions of storage
The preparation should be stored in a dark place, out of the reach of children, at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Shelf life - 4 years.
Do not use after expiration date.