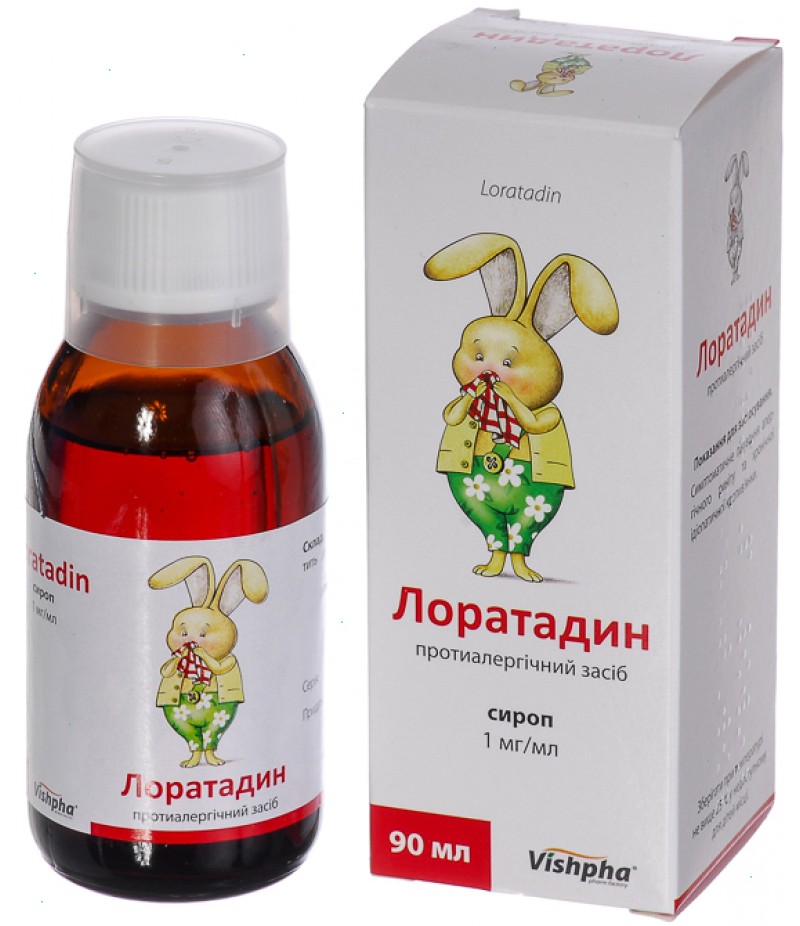
Loratadine syrup 5 mg / 100 ml
- $9.47
- Availability:In Stock
Loratadine syrup instuction for useYou can buy Loratadine syrup heregeneral characteristicsinternational and chemical names: loratadine; 4- [8-chloro-5,6-dihydro-1 [H-benzo [5,6] cyclohepta [1,2-v] pyridin- [1-ylidene] -1-piperidi..
Tags: syrup
Loratadine syrup instuction for use
You can buy Loratadine syrup here
general characteristics
international and chemical names: loratadine; 4- [8-chloro-5,6-dihydro-1 [H-benzo [5,6] cyclohepta [1,2-v] pyridin- [1-ylidene] -1-piperidinecarboxylic acid ethyl ester;
basic physical and chemical properties: colorless or slightly
yellowish, or slightly greenish-yellowish liquid with a specific odor;
composition: 5 ml of syrup contains - 5 mg of loratadine;
auxiliary substances: refined sugar, citric anhydrous acid, sodium
benzoate, propylene glycol, glycerin, food aroma "Apricot 059", purified
water.
Form of issue. Syrup.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Antihistamines. ATS code R06A X13.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics. Loratadine is a tricyclic piperidine compound with a pronounced antihistamine effect; has selective antagonism with respect to peripheral histamine H1-receptors. Loratadine
is a long-acting drug that exhibits a complex effect, including
antiallergic, antipruritic and antiexcudative activity, reduces
permeability of capillaries, prevents the development of edema of
tissues, eliminates spasms of smooth muscles. The drug and its metabolites do not penetrate the blood-brain barrier. Loratadine does not have a sedative effect.
Pharmacokinetics. After ingestion, the drug is found in the blood after 15 to 20 minutes. The
maximum concentration of Loratadine and its metabolite of
decarboxetoxyloratadine in plasma is observed after 1 hour and persists
to 36-48 hours. Approximately 97% of Loratadine binds to plasma proteins. The drug penetrates into breast milk, is excreted in urine and feces.
Indications for use
Allergic rhinitis (seasonal and year-round), allergic conjunctivitis, acute and chronic urticaria, Quincke's edema, allergic reactions to insect bites, pseudoallergic reactions to histamine-liberators, as well as contact allergic dermatitis and chronic eczema.
Dosing and Administration
The drug is administered to adults and children older than
12
years - 10 mg 2 teaspoons (10 ml) once a day, children aged 2 to 12
years with a body weight of less than 30 kg - 5 mg 1 teaspoon (5 ml),
with a body weight of more than 30 kg - 10 mg 2 teaspoons (10 ml) once a day. The course of treatment is 5-10 days.
Side effect
In the application of Loratadin in isolated cases, headache, dry
mouth, drowsiness, nausea, allergic reactions in the form of a rash can
be observed.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to loratadine or some other component of the syrup. Children up to 2 years.
Overdose
When the therapeutic doses of Loratadine exceed 4 and more times, the
risk of side effects increases: drowsiness, tachycardia and headache.
Application features
Loratadine is not a sedative antihistamine, but some patients may have a dose-dependent sedative effect. The
drug should be administered with caution to persons whose work is
related to the management of transport or other mechanisms. In
patients with impaired liver function or renal insufficiency, the
initial dose of the drug should be 10 mg (2 teaspoons of syrup) every
other day. During
pregnancy and lactation, the drug should be used only if the
therapeutic effect of its use in the mother exceeds the potential risk
to the fetus or newborn.
Interaction with medicines
With the simultaneous use of loratadine with cimetidine, erythromycin,
ketoconazole, it is possible to increase its serum concentration caused
by a disruption in the metabolism of Loratadin, probably due to the
inhibition of cytochrome isoenzyme CYP3A4
P-450.
In connection with the possible development of a dose-dependent
sedative effect, caution should be exercised while using Loratadine with
other H1 receptor blockers, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, opioid
receptor agonists, neuroleptics, tricyclic antidepressants, sedatives
and hypnotics.